APSF Technology Education Initiative (TEI) : Quantitative Neuromuscular Monitoring (QNM)
| Table of Contents |
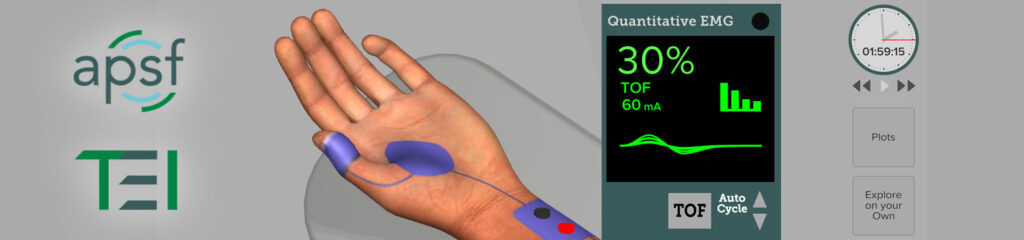
This quantitative neuromuscular monitoring (QNM) course consists of six topics designed to empower the anesthesia professional with the knowledge required to safely and effectively use QNM. The QNM course is largely aligned with the ASA 2023 Practice Guidelines for Monitoring and Antagonism of Neuromuscular Blockade. The six topics are: 1) Introduction to QNM, 2) Obtaining Baseline Train-of-Four Ratio, 3) Qualitative vs Quantitative Neuromuscular Assessment of Blockade Depth, 4) Achieving and Monitoring Intubating Conditions, 5) QNM During Maintenance and 6) QNM During Antagonism and Recovery from NMB. Each topic is designed for about a 15 minute interaction but the motivated learner is encouraged to utilize the simulation platform to explore different strategies and reinforce the learning. The topics are designed to be followed in sequence but do not need to be done at the same time. The course is free of charge to all anesthesia professionals; a free guest login is required for non-ASA members.
- Click here to take the Quantitative Neuromuscular Monitoring course on the ASA website
(This link navigates away from the APSF website to the ASA website to sign-in and access the course.)
Courses are available to any learner at no cost. All courses are delivered through the ASA learning management system.ASA members can use member login credentials.Non-ASA members can create an ASA account at no charge.
To create an ASA login and access the courses follow these steps:
- Click HERE to create an ASA account.
- Sign in to the ASA account.
- Return to the APSF webpage for the course of interest and click the link to take the course on the ASA website.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES ON QUANTITATIVE NEUROMUSCULAR MONITORING
- Monitoring Depth of Neuromuscular Blockade
by Steven Haberkorn, BA; Debra J Faulk, MD
Residual neuromuscular blockade is frequent in anesthesia practice and can lead to adverse outcomes. This keyword summary reviews the problem of residual weakness, the ways in which we can subjectively and objectively assess the neuromuscular junction for adequate return of strength, and summarizes recommendations in the 2023 ASA practice guidelines for monitoring and antagonism of neuromuscular blockade.
QUANTITATIVE NEUROMUSCULAR MONITORING VENDORS IN THE US
Thank You to the 2025 APSF Corporate Advisory Council Members/Corporate Donors

Blink
https://www.blinkdc.com/twitchview-user-guide

Dräger
https://www.draeger.com/Products/Content/tofscan-pi-9017131-en-us-1904-1.pdf
![]()
GE
https://clinicalview.gehealthcare.com/video/emg-based-nmt-monitoring-ge-healthcare-solution
![]()
Nihon Kohden
https://us.nihonkohden.com/products/smart-cable-nmt-pod/
Other Vendors
Philips
RGB Medical Devices
Senzime
Xavant
APSF does not promote or recommend any particular device or manufacturer. APSF does partner with companies interested in supporting the APSF mission through membership in the APSF Corporate Advisory Council. Links to manufacturer websites are provided by APSF partners and intended to provide a convenience for professionals interested in additional education on specific devices. For completeness, APSF also provides the names of companies who supply in the United States technology relevant to the educational topic.
